3 reasons the Willow oil drilling project in Alaska’s Arctic was approved
It’s the latest battle in a long fight over Alaska’s North Slope.
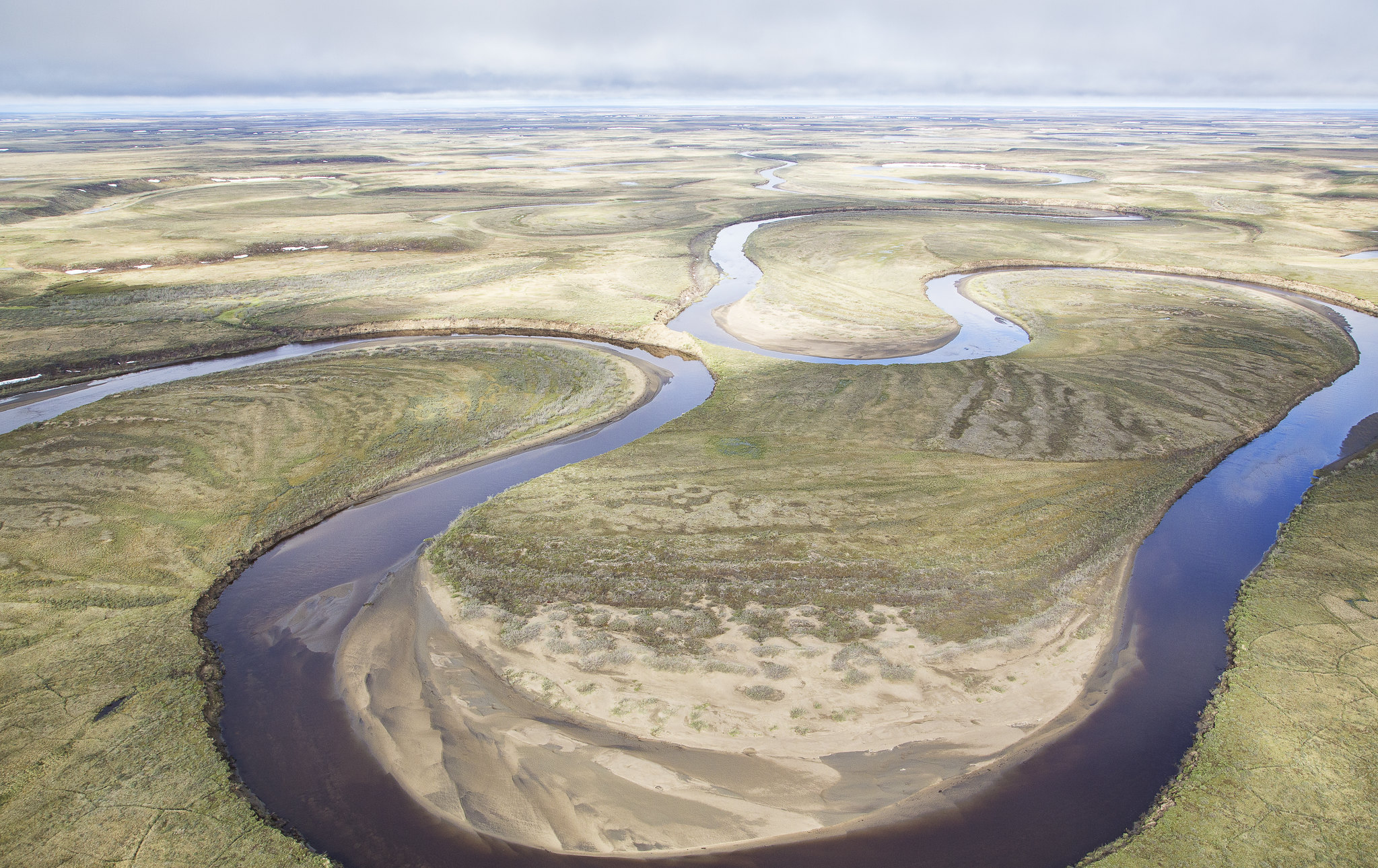

For more than six decades, Alaska’s North Slope has been a focus of intense controversy over oil development and wilderness protection, with no end in sight. Willow field, a 600-million-barrel, $8 billion oil project recently approved by the Biden administration — to the outrage of environmental and climate activists — is the latest chapter in that long saga.
To understand why President Joe Biden allowed the project, despite vowing “no more drilling on federal lands, period” during his campaign for president, some historical background is necessary, along with a closer look at the ways domestic and international fears are complicating any decision for or against future oil development on the North Slope.
More than just Willow
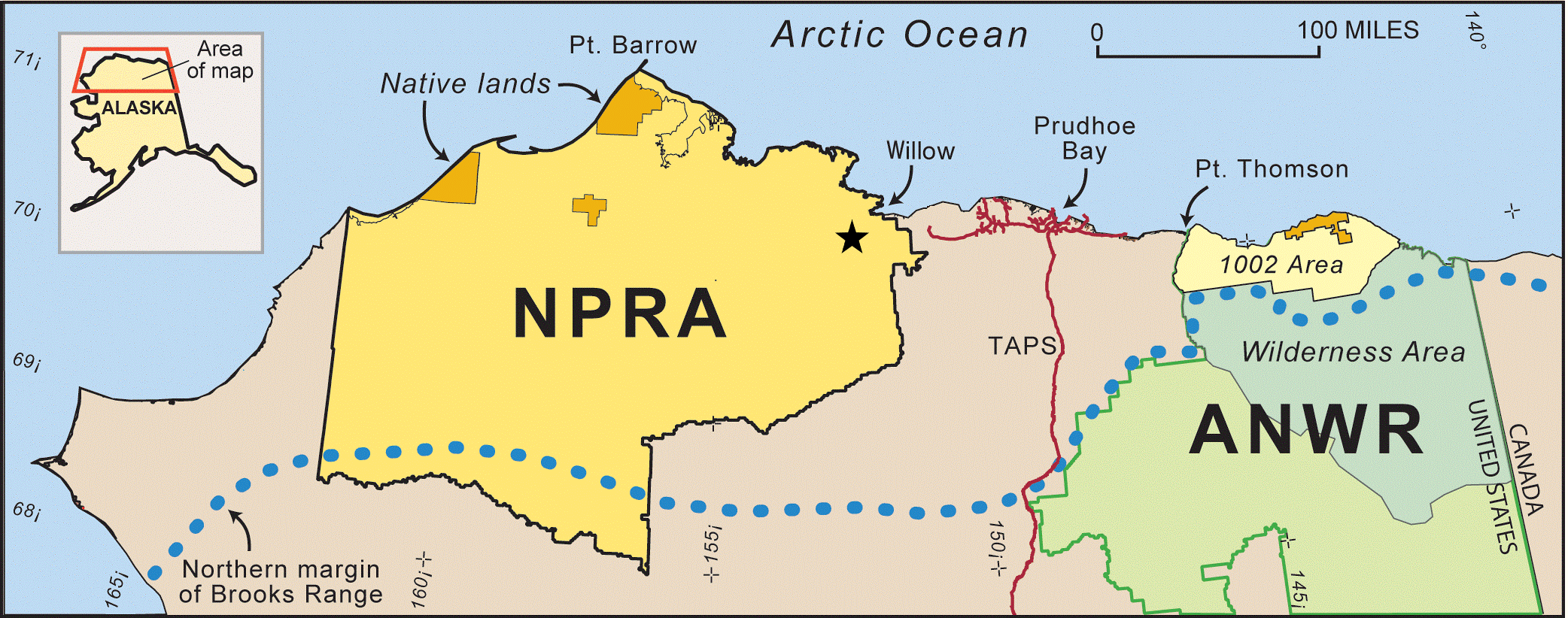
The Willow project lies within a vast, 23 million-acre area known as the National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska, or NPR-A. This was one of four such reserves set aside in the early 1900s to guarantee a supply of oil for the U.S. military. Though no production existed at the time in NPR-A, geologic information and surface seeps of oil suggested large resources across the North Slope.
Proof came with the 1968 discovery of the supergiant Prudhoe Bay field, which began producing oil in 1977. Exploratory programs in the NPR-A, however, found only small oil accumulations worthy of local uses.
Then, in the 2000s, new geologic understanding and advanced exploration technology led companies to lease portions of the reserve, and they soon made large fossil fuel discoveries. Because NPR-A is federal land, government approval is required for any development. To date, most have been approved. Willow is the latest.
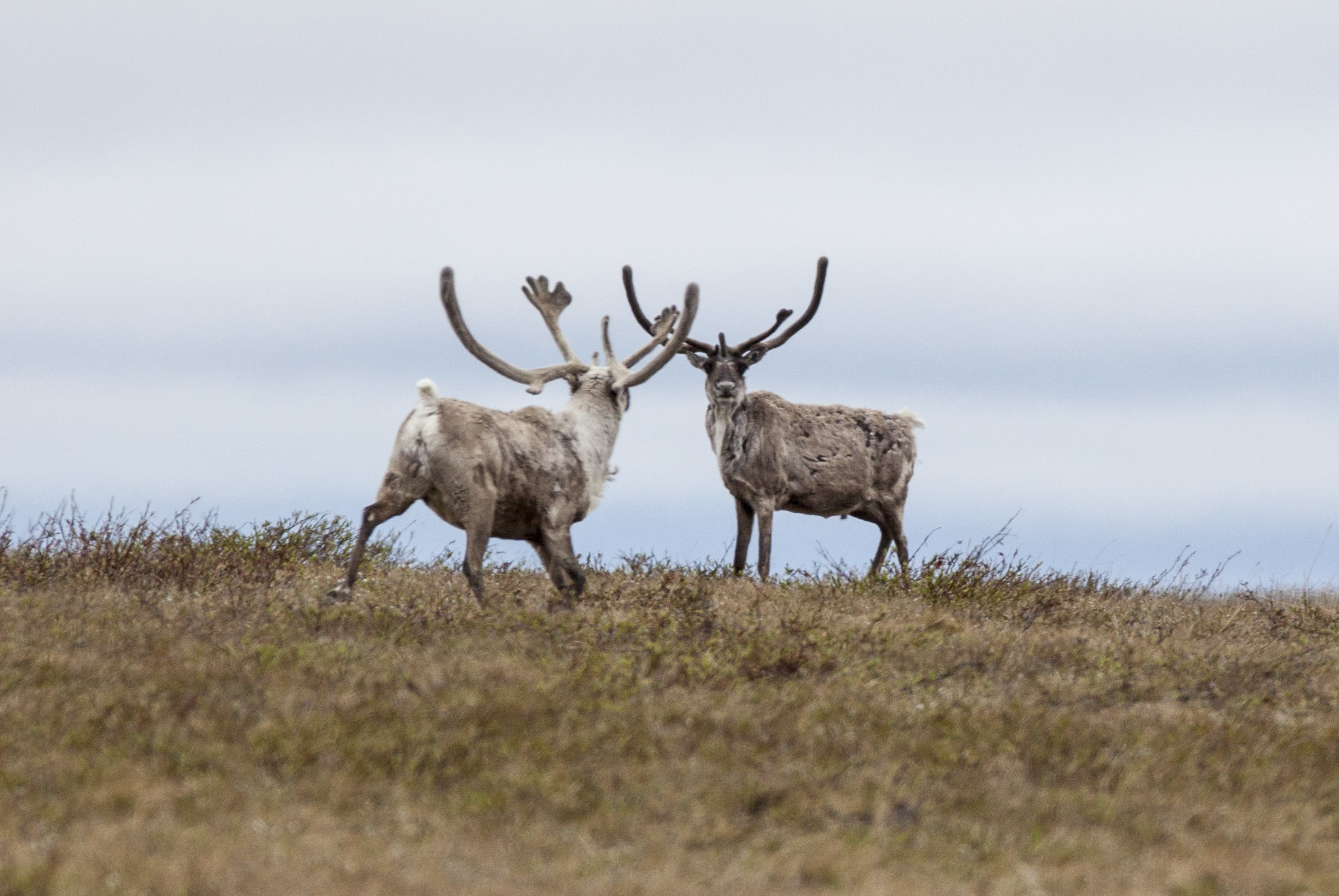

Opposition to North Slope drilling from conservationists, environmental organizations and some Native communities, mainly in support of wilderness preservation, has been fierce since the opening of Prudhoe Bay and the construction of the trans-Alaska pipeline in the 1970s. In the wake of 1970s oil crises, opponents failed to stop development.
During the next four decades, controversy shifted east to the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge. Republican presidents and congressional leaders repeatedly attempted to open the refuge to drilling but were consistently stifled — until 2017. That year, the Trump administration opened it to leasing. Ironically, there was very little interest. Oil prices had fallen, risk was high and the reputational cost was large.
To the west of the refuge, however, a series of new discoveries in NPR-A and adjacent state lands were drawing attention as a major new oil play with multibillion-barrel potential. Oil prices had risen, and though they fell again in 2020, they have been mostly above $70 per barrel – high enough to encourage significant new development.
Opposition, with little success
Opposition to the new Willow project has been driven by concerns about the effects of drilling on wildlife and of increasing fossil fuel use on the climate. Willow’s oil is estimated to be capable of releasing 287 million metric tons of carbon dioxide if refined into fuels and consumed.
In particular, opponents have focused on a planned pipeline that will extend the existing infrastructure further westward, deeper into NPR-A, and likely encourage further exploratory drilling.
So far, that resistance has had little success.
Twenty miles to the south of Willow is the Peregrine discovery area, estimated to hold around 1.6 billion barrels of oil. Its development was approved by the Biden administration in late 2022. To the east lies the Pikka-Horseshoe discovery area, with around 2 billion barrels. It’s also likely to gain approval. Still other NPR-A drilling has occurred to the southwest (Harpoon prospect), northeast (Cassin), and southeast (Stirrup).
Questions of legality
One reason the Biden administration approved the Willow project involves legality: ConocoPhillips holds the leases and has a legal right to drill. Canceling its leases would bring a court case that, if lost, would set a precedent, cost the government millions of dollars in fees and do nothing to stop oil drilling.
Instead, the government made a deal with ConocoPhillips that shrank the total surface area to be developed at Willow by 60%, including removing a sensitive wildlife area known as Teshekpuk Lake. The Biden administration also announced that it was putting 13 million acres of the NPR-A and all federal waters of the Arctic Ocean off limits to new leases.
That has done little to stem anger over approval of the project, however. Two groups have already sued over the approval.
Taking future risks into account
To further understand Biden’s approval of the Willow project, one has to look into the future, too.
Discoveries in the northeastern NPR-A suggest this will become a major new oil production area for the U.S. While actual oil production is not expected there for several years, its timing will coincide with a forecast plateau or decline in total U.S. production later this decade, because of what one shale company CEO described as the end of shale oil’s aggressive growth.
Historically, declines in domestic supply have brought higher fuel prices and imports. High gasoline and diesel prices, with their inflationary impacts, can weaken the political party in power. While current prices and inflation haven’t damaged Biden and the Democrats too much, nothing guarantees this will remain the case.
Geopolitical concerns, particularly Europe
The Biden administration also faces geopolitical pressure right now due to Russia’s war on Ukraine.
U.S. companies ramped up exports of oil and natural gas over the past year to become a lifeline for Europe as the European Union uses sanctions and bans on Russian fossil fuel imports to try to weaken the Kremlin’s ability to finance its war on Ukraine. U.S. imports have been able to replace a major portion of Russian supply that Europe once counted on.
Europe’s energy crisis has also led to the return of energy security as a top concern of national leaders worldwide. Without a doubt, the crisis has clarified that oil and gas are still critical to the global economy. The Biden administration is taking the position that reducing the supply by a significant amount — necessary as it is to avoid damaging climate change — cannot be done by prohibition alone. Halting new drilling worldwide would drive fuel prices sky high, weakening economies and the ability to deal with the climate problem.
Energy transitions depend on changes in demand, not just supply. As an energy scholar, I believe advancing the affordability of electric vehicles and the infrastructure they need would do much more for reducing oil use than drilling bans. Though it may seem counterintuitive, by aiding European economic stability, U.S. exports of fossil fuels may also help the EU plan to accelerate noncarbon energy use in the years ahead.
Scott L. Montgomery is a lecturer at Jackson School of International Studies at University of Washington.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
This article has been fact-checked by Arctic Today and Polar Research and Policy Initiative, with the support of the EMIF managed by the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation.
Disclaimer: The sole responsibility for any content supported by the European Media and Information Fund lies with the author(s) and it may not necessarily reflect the positions of the EMIF and the Fund Partners, the Calouste Gulbenkian Foundation and the European University Institute.
